Artificial Intelligence
- Home
- Artificial Intelligence
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the branch of computer science focused on creating systems and machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, decision-making, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. AI systems simulate human cognitive processes to solve complex problems efficiently.
Core Features of Artificial Intelligence
Automation:
- AI automates repetitive and complex tasks, increasing efficiency.
- Example: Automated customer support via chatbots.
Learning and Adaptation:
- AI systems learn from data to improve their performance over time.
- Example: Recommendation algorithms for Netflix or Amazon.
Reasoning:
- AI can analyze information and make decisions based on logic.
- Example: Fraud detection in financial transactions.
Natural Interaction:
- AI enables natural communication with users via text or speech.
- Example: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
Problem Solving:
- AI can identify patterns and solve complex problems faster than humans.
- Example: AI-driven drug discovery.
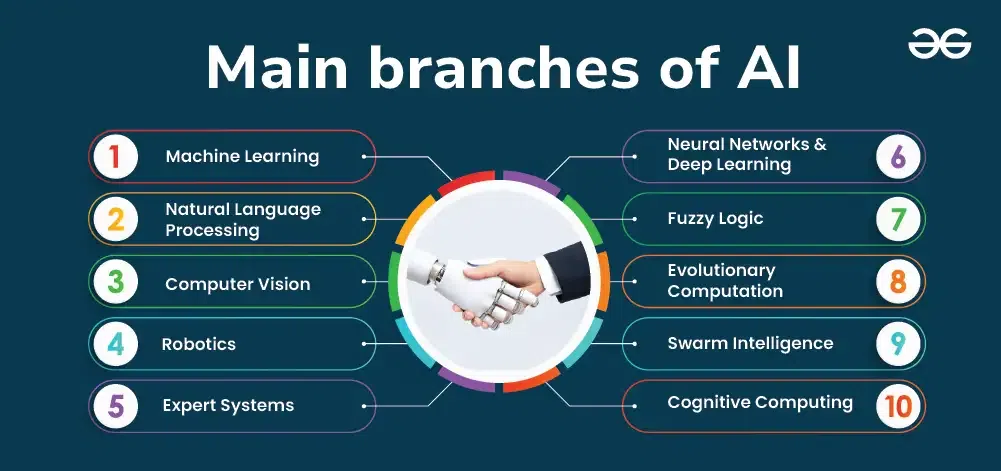
Key Categories of Artificial Intelligence
Narrow AI (Weak AI):
- Designed to perform a specific task or solve a specific problem.
- Examples: Spam filters, recommendation systems, weather prediction.
General AI (Strong AI):
- Theoretical AI capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can do.
- Not yet achieved in current technology.
Superintelligent AI:
- Hypothetical AI surpassing human intelligence in all domains.
- Considered a future possibility, with ethical concerns surrounding it.
Subfields of AI
1.Machine Learning (ML):
- Focuses on algorithms that enable machines to learn and improve from data.
- Example: Predictive analytics in business.
Deep Learning:
- A subset of ML using neural networks to mimic human brain functionality.
- Example: Image recognition systems.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Example: Language translation apps.
Computer Vision:
- Focuses on enabling machines to interpret visual data from the world.
- Example: Face recognition software.
Robotics:
- Combines AI with hardware to develop machines that perform physical tasks.
- Example: Warehouse robots used by Amazon.
Applications of AI
Healthcare:
- AI-powered diagnostic tools, robotic surgery, personalized treatment.
- Example: AI systems analyzing radiology images for cancer detection.
Finance:
- Fraud detection, automated trading, customer credit scoring.
- Example: AI-powered chatbots in banking for customer queries.
Transportation:
- Self-driving cars, traffic optimization, route planning.
- Example: Tesla’s Autopilot system.
Retail and E-commerce:
- Product recommendations, inventory management, dynamic pricing.
- Example: Personalized shopping experiences on e-commerce platforms.
Education:
- Adaptive learning platforms, automated grading, virtual tutors.
- Example: AI-powered platforms like Khan Academy.
Entertainment:
- Content curation, realistic animations, gaming AI.
- Example: Spotify’s personalized playlists.
Manufacturing:
- Predictive maintenance, quality control, robotics in assembly lines.
- Example: AI used by BMW to ensure production accuracy.

Agriculture:
- Crop monitoring, pest detection, yield prediction using drones and sensors.
- Example: AI-enabled precision farming.
Energy:
- Smart grids, energy consumption optimization, renewable energy management.
- Example: Predictive analytics for solar panel maintenance.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Efficiency and Automation:
- Automates repetitive tasks, saving time and resources.
Accuracy and Precision:
- Reduces errors in critical applications, such as medical diagnoses.
24/7 Availability:
- Operates continuously without breaks or fatigue.
Scalability:
- Handles vast amounts of data and complex tasks.
Enhanced Decision-Making:
- Analyzes data quickly to provide insights for better decisions.
Challenges and Concerns
Ethical Issues:
- Concerns about data privacy, surveillance, and AI bias.
Job Displacement:
- Automation may lead to job losses in certain sectors.
Security Risks:
- Vulnerability to hacking and malicious use of AI systems.
Lack of Transparency:
- Complex AI models (e.g., deep learning) are often difficult to interpret.
Regulation and Governance:
- Lack of clear frameworks for AI use and accountability.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
General AI Development:
- Research aimed at building systems capable of human-like reasoning.
AI in Everyday Life:
- Wider adoption in homes, workplaces, and public services.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
- Collaboration between AI, blockchain, and quantum computing.
Ethical and Sustainable AI:
- Focus on building responsible and fair AI systems.
Enhanced Personalization:
- AI-driven solutions tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming industries, improving efficiency, and unlocking new possibilities across the globe. Its potential to address complex challenges and enhance human capabilities is immense. However, as AI continues to evolve, it is crucial to address ethical and societal concerns to ensure its development benefits humanity as a whole.
