IOT
- Home
- IOT
What is IoT (Internet of Things)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices and objects that communicate with each other over the internet. These devices are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, allowing them to collect, exchange, and act on data, often without human intervention.
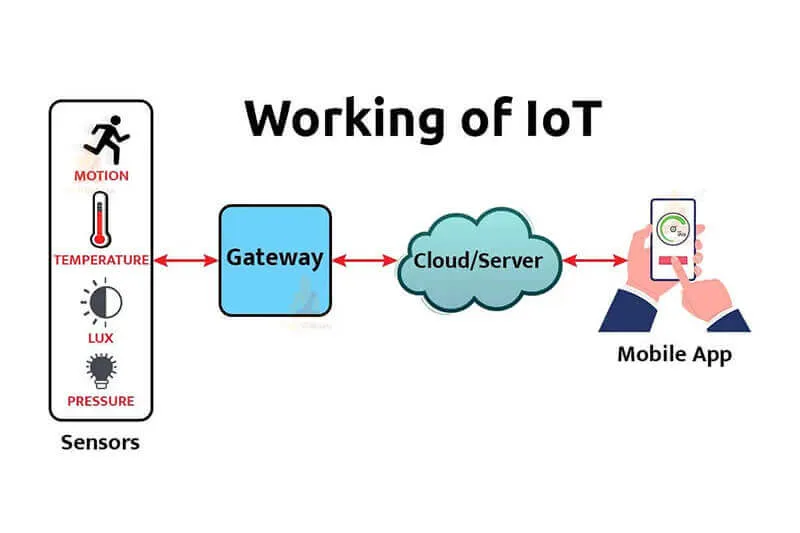
How IoT Works
Sensors and Devices:
- IoT devices are equipped with sensors to collect data (e.g., temperature, motion, humidity).
Connectivity:
- Data from these devices is transmitted over the internet or local networks using protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee.
Data Processing:
- The collected data is sent to cloud servers or edge devices for processing and analysis.
Action:
- Based on the data analysis, IoT systems can take actions, send notifications, or provide insights.
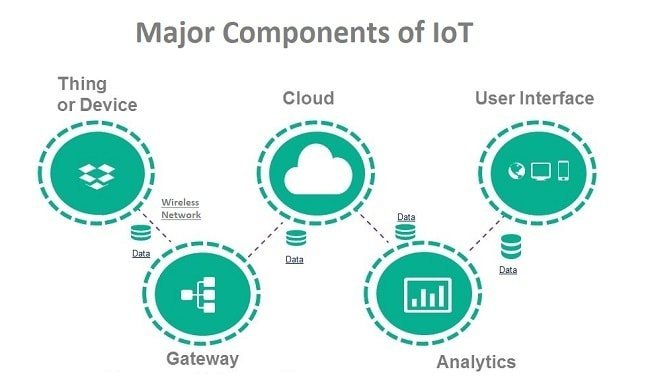
Key Components of IoT
IoT Devices:
- Physical objects such as smart thermostats, wearable devices, and industrial sensors.
Network:
- Communication protocols and technologies that connect devices to the internet (e.g., Wi-Fi, LTE, 5G).
Cloud Platforms:
- Centralized platforms to store and process data (e.g., AWS IoT Core, Microsoft Azure IoT).
Data Analytics:
- Tools that analyze the data collected from devices to provide actionable insights.
User Interfaces:
- Applications or dashboards for users to interact with IoT systems.
Applications of IoT
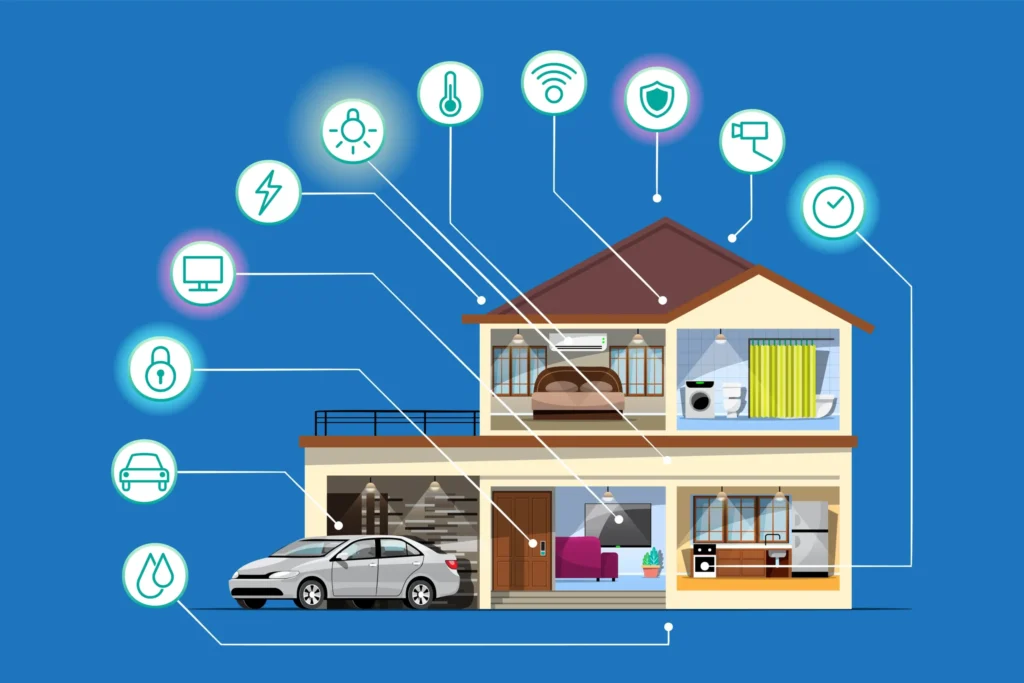
Smart Homes:
- Devices like smart lights, thermostats, and security cameras.
- Example: Amazon Echo or Google Nest.
Healthcare:
- Wearable devices for health monitoring (e.g., Fitbit, glucose monitors).
- Example: Remote patient monitoring systems.
Transportation:
- Connected cars, GPS trackers, and traffic management systems.
- Example: Tesla’s Autopilot.
Agriculture:
- Smart irrigation, soil sensors, and crop monitoring.
- Example: Drones for crop surveillance.
Industrial IoT (IIoT):
- Predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and automation.
- Example: Smart factories.
Retail:
- Inventory tracking, personalized marketing, and smart checkout systems.
- Example: Amazon Go stores.
Energy Management:
- Smart grids, energy consumption monitoring, and renewable energy integration.
- Example: Smart meters.
Smart Cities:
- Solutions like traffic management, waste management, and smart lighting.
- Example: Parking sensors in urban areas.

Advantages of IoT
Automation and Control:
- Reduces human intervention and improves efficiency.
Cost Savings:
- Helps optimize resource use (e.g., energy, water).
Data-Driven Insights:
- Provides real-time data for better decision-making.
Convenience:
- Enhances user experience with automated solutions.
Improved Safety:
- Enables monitoring and alerts for potential hazards.
Challenges of IoT
Security Concerns:
- Devices are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches.
Data Privacy:
- Collecting large amounts of personal data raises ethical concerns.
Interoperability:
- Lack of standardization across IoT devices and platforms.
Cost of Implementation:
- High initial costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure.
Scalability:
- Managing a large number of connected devices can be complex.
Future Trends in IoT
5G Connectivity:
- Faster and more reliable IoT communication.
Edge Computing:
- Processing data closer to the source (devices) to reduce latency.
AI Integration:
- Using AI for smarter automation and predictive analytics.
IoT in Healthcare:
- Advanced remote monitoring and robotic surgeries.
Blockchain for IoT:
- Enhancing security and transparency in data exchanges.
Green IoT:
- Sustainable and energy-efficient IoT solutions.
Why IoT is Important
Transformative Potential: IoT has the power to revolutionize industries by increasing efficiency and enabling new business models.
Enhanced Lifestyle: IoT improves the quality of life through smart devices and connected systems.
Economic Impact: IoT is expected to contribute trillions to the global economy by 2030.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping how we interact with the physical and digital worlds. From smart homes to industrial applications, IoT offers immense possibilities to enhance productivity, convenience, and safety. However, as it grows, addressing challenges like security, scalability, and standardization will be crucial for its sustainable adoption.
